
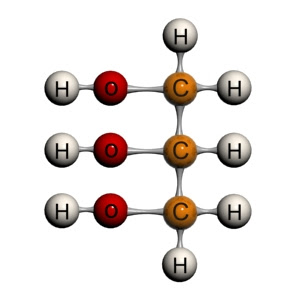
Lipogenesis is the process of producing lipid or fat. 1 This structure makes glycerol highly hygroscopic (readily attracts moisture) and soluble in water and in alcohol. It is a trihydric alcohol since it is comprised of three carbon atoms each of the two end carbon atoms is bound to two hydrogen atoms and a hydroxyl group the central carbon atom is bound to a hydrogen atom and a hydroxyl group. Glycerol is a colorless, odorless, viscous, sweet-tasting polyol with a chemical formula of C 3H 8O 3. For instance, the glycerin syrup is 99.7% glycerol. Nevertheless, the term “glycerol” is often used to indicate the presence of the compound as an ingredient of a product whereas “glycerine” (or glycerin) often pertains to the product name. 3 Glycerol is also called glycerine (or glycerin).
As a food additive, glycerol has been approved as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS) by US Food and Drug Administration (FDA). 2 Today, glycerol is artificially synthesized for its various uses in food, medicine, and other industries. In 1872, it was first synthesized inside a laboratory by the French chemist Charles Friedel 1832–1899. In 1836, the French chemist Théophile-Jules Pelouze 1807-1867 determined its chemical formula (C 3H 8O 3). Etymologically, glycerol came from the Greek glycos, meaning “sweet”. 1 Its name glycerol was coined by the French chemist Michel Eugéne Chevreul 1786–1889. In olive oil, glycerol is the predominant triglyceride. He obtained glycerol when the glycerol was washed out of a heated mixture of lead oxide and olive oil. Glycerol was discovered in 1779 by the Swedish chemist Carl Wilhelm Sheele 1742-1786.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
